Use these questions to test your understanding. If you get them wrong, you will be linked back to the relevant part of the notes.
Use these questions to test your understanding. If you get them wrong, you will be linked back to the relevant part of the notes.
Be sure you study them thoroughly (don't just get a quick fix for your mistake) so your overall understanding is improved.
1. A white dwarf does not collapse further because
a. it is converting H to He b. it is converting He to C
c. its electrons can't be squeezed together any more d. it is made of dark matter
2. Pulsars vary their light output by
a. alternately expanding and contracting b. alternately heating up and cooling off
c. sweeping a light beam across our line of sight d. converting H to He
3. Planetary nebulae are
a. in the process of forming planets b. molecular clouds
c. the ejected outer layers of a dying star d. the precursors to black holes
e. the result of protostars having disks
4. A neutron star is mostly neutrons because
a. the protons it used to contain have collected into a proton star
b. it has a proton core, but neutrons cover the surface
c. the huge pressure has caused its electrons to merge with its protons to make neutrons
d. antiprotons have annihilated all the protons it used to contain
e. the protons have collapsed into a black hole in its core
5. If you add mass to a white dwarf to "bulk it up" above 1.4 solar masses,
a. it will get smaller and smaller and finally collapse into a neutron star
b. it will develop strong coronal lines because of its high surface temperature
c. it will increase in radius in proportion to the cube root of the additional mass
d. the new matter will cause it to cool on the surface and get fainter
e. the matter will disappear beyond its event horizon and we will not know what happens
6. The most important aspect (to us) of the material ejected by dying stars is
a. it makes beautiful nebulae that inspire our interest in astronomy
b. it shields us from dangerous radiation emitted by the dying star itself
c. it reduces the mass of the star so its end is less violent
d. we are made of material ejected by dying stars a long time ago
e. it causes interstellar extinction
The next five questions refer to the following graph.
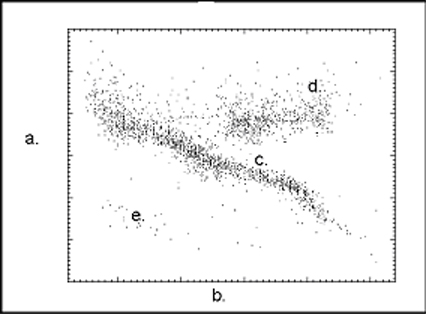
7. Which letter indicates where giant stars would be found in the HR diagram?
8. Which indicates the location of white dwarfs?
9. Which indicates where spectral type would be found?
10. Which indicates the location of the main sequence?
11. Which indicates where luminosity would be found?