The Galactic Center -- Nucleus of the Milky Way
Key points: How the Galactic Center was hidden; evidence for a black hole AND for recent star formation; the circumnuclear ring
Conditions for star formation and evolution must be very
different in the centers of galaxies. If we lived in the center of a galaxy, there would be a million
stars between us and another star at 1 parsec distance such as alpha Centaurus. In our
actual position, alpha Centaurus is the closest star. This huge density of stars may cause
peculiar things to happen to them as they form and evolve. In addition, centers of galaxies harbor ultramassive
(up to a billion M![]() ) black holes that we
see as quasars or bright radio galaxies, exotic objects that make huge amounts of energy.
Conditions around them must be so extreme, they test our laws of physics.
) black holes that we
see as quasars or bright radio galaxies, exotic objects that make huge amounts of energy.
Conditions around them must be so extreme, they test our laws of physics.
In the nearest galaxies, the highest resolution pictures we have taken show details only down to 10 to 30 light years. With perhaps 100,000,000 stars lumped together, we can barely see even the brightest individual stars. Also, we cannot study what happens really close to any possible black hole.
The center of the Milky Way is 100 times closer than the next closest galactic nucleus, so we can take pictures showing details 0.03 light years in size. This "cosmic zoom lens" makes the Galactic Center have an importance for galaxy studies similar to the importance of the sun for stellar work.
However, extinction makes the Galactic Center inaccessible to visible-light astronomy. It was located approximately by radio measurements, then definitively in the starlight at 2 microns.
 |
The central few hundred parsecs in visible light: the view is dominated by thick obscuring clouds in the disk of the Milky Way. |
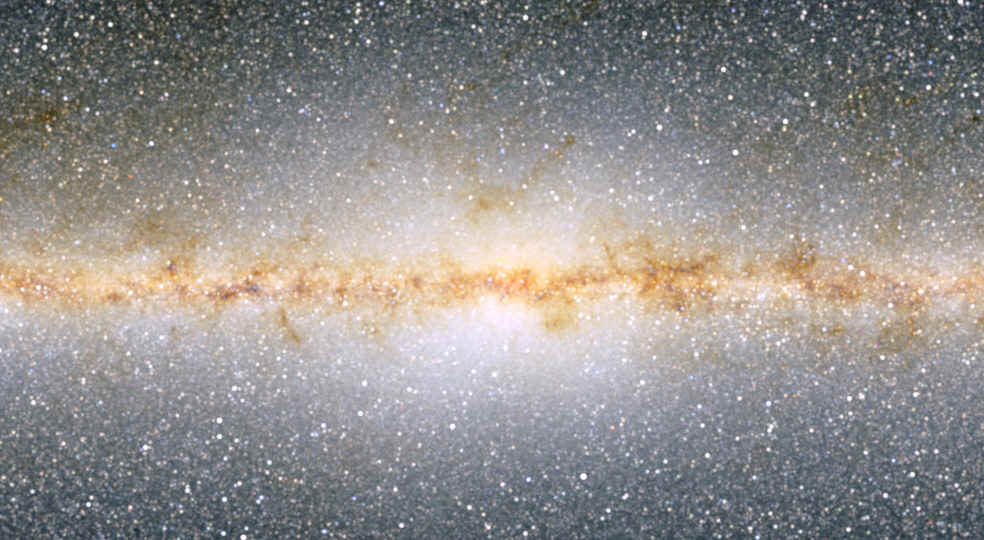 |
The central few hundred parsecs in near-infrared light: what a difference! We see through most of the dust to get an impression of what the galaxy is really like. (2MASS Project, http://www.ipac.caltech.edu/2mass/gallery/showcase/allsky_stars/fullres.html) |
 |
A bit farther into the infrared cuts through the dust even better and shows the center more clearly. (from NASA/JPL-Caltech/S. Stolovy (Spitzer Science Center) |
 |
An infrared image about 10 parsecs across shows lots of very luminous stars and leaves little doubt where the true center lies (From M. & G. Rieke). |
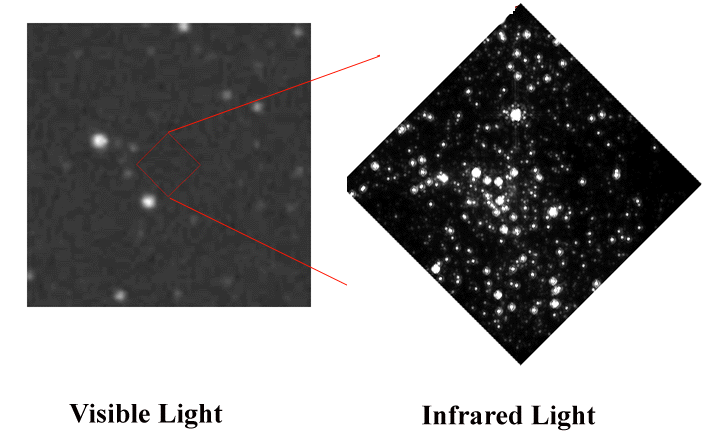 |
Even knowing exactly where to look does not help in the visible -- there are just a few foreground stars that lie in front of the heavy clouds of obscuring dust that hide the real center. |
 |
The region is a dramatic radio source. Here is the central roughly hundred parsecs in the radio. The Galactic Center itself is the bright source to the lower right. The arcs are thought to be hot gas flowing along a strong magnetic field.(From F. Yussef-Zadeh, VLA, APOD, http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap020521.html) |
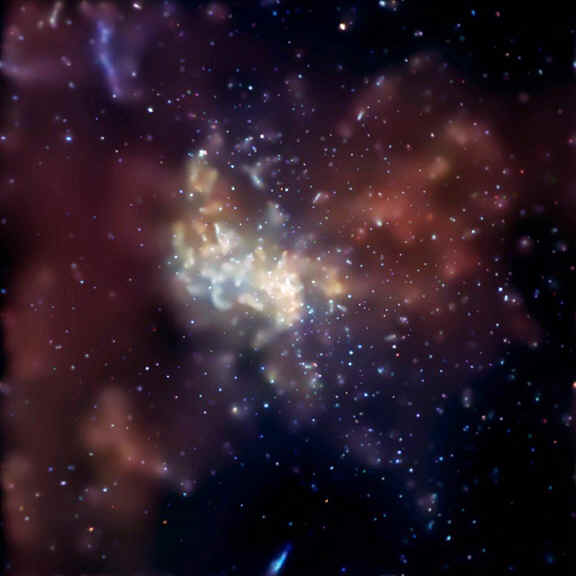 |
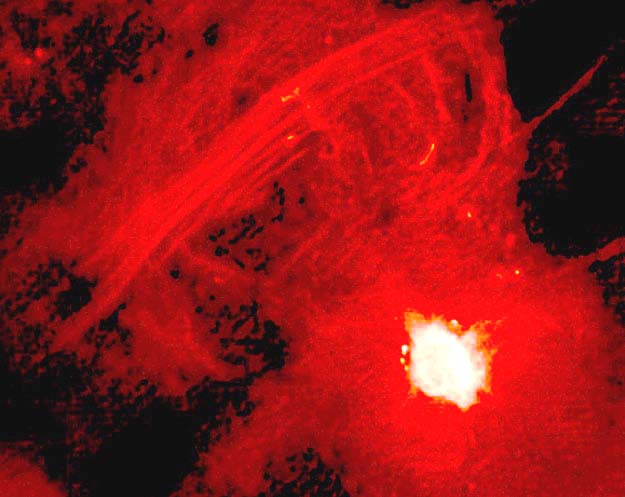
Here is a very deep, high resolution (1 arcsec) X-ray image of the Galactic Center -- the source elongated up and down just above and to the right of the center is Sgr A*, but it doesn't stand out at all. Even in X-rays, where we look to find stellar black holes, there is nothing to draw our attention to a supermassive black hole here!(from NASA/CXC/MIT/F.K.Baganoff et al. http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2003/0203long/index.html) |
However, we can see the black hole faintly in the radio!
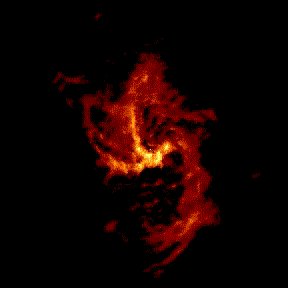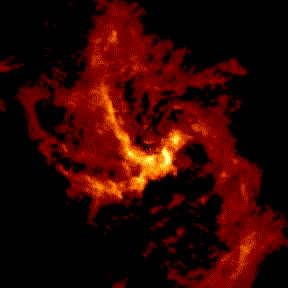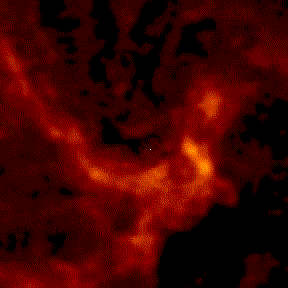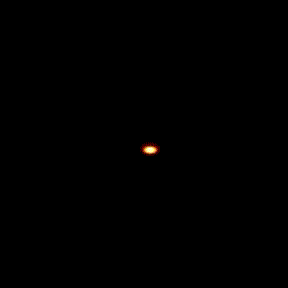 |
Starting from a large scale radio image, let's zoom in on Sgr A*. We start with a view about 2 parsecs across; if we put the sun at the center, the nearest star would be near the edge, but in the Galactic Center the frame is filled with millions of stars (none of which can be seen in the radio image). We zoom in by a factor of about 1,000 to see the Sgr A* radio source just barely resolved by our highest resolution radio measurements. animation from Melia, Falcke, and Agol |
Can we prove there is a black hole?????
We have measured enough velocities of stars to measure the gravitational field accurately. Even if it doesn't make much energy, and is virtually invisible, it turns out there is a very massive (more than 3 million sun masses) black hole right in the center.
 |
Although it is too dim to detect most of the
time, once in a while the black hole flares up - presumably because
something has fallen into it and energy has been released as a result! (from UCLA Galactic Center Group, http://www.galacticcenter.astro.ucla.edu/animations.html)
Here is an animation of a what may be going on: The biggest flares we have seen correspond to a Mercury-sized object getting swallowed up. http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2007/gcle/ A much bigger flare may have occurred 500 years ago, when briefly we might have had an active galactic nucleus (discussed on the next page)! http://m.technologyreview.com/blog/arxiv/27159/
|
The lack of energy from the Galactic Center black hole has turned out to be a major challenge to our theories of black holes. We think that the matter surrounding the black hole in the Galactic Center is very hot and in a sphere rather than a disk, and virtually transparent to its own radiation so it does not heat up efficiently. The energy is not emitted in the X-ray, but is carried inward by the flow of matter toward the event horizon.
 |
Here is a radio image of the central 5 x 5 parsecs of the Milky Way. Sgr A* is near the center of the bright, complex source to the right. Because of its appearance, this structure is called the "minispiral." Sgr A* is not clearly visible on this image, which emphasizes much larger structures. (from http://www.astro.utu.fi/~cflynn/galdyn/l13.html) |
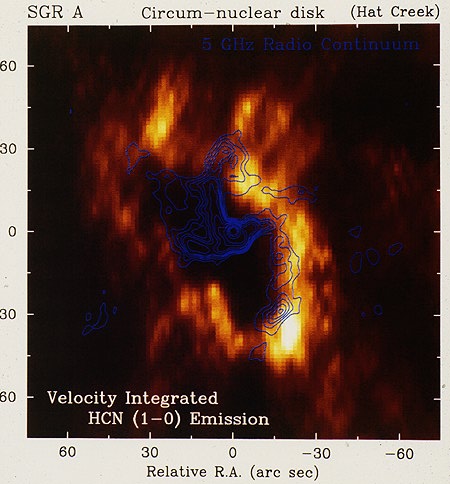 |
Here is an image in the emission of the HCN molecule, shown in yellow and orange. We see a ring of molecular material (diameter about 2 parsecs) surrounding the black hole. It is shown here imaged in a radio molecular emission line, but it shows up in other ways too. The minispiral is superimposed in blue contours. It appears to be filaments of gas falling inward from the molecular ring. |
What is the Energy Source?
The center of the molecular ring is filled with young stars. Why did these stars form, rather than the material falling into the black hole and making it a bright source? We do not know the answer for sure. Spectra show many of the brightest sources are normal red supergiants. As a result, we conclude we are seeing the normal stages of evolution of massive stars. Stars must have formed in the Galactic Center in the last 10 million years, since that is how long it would take to evolve to the red supergiant.
|
|

Marvel Quasar Comic, http://www.coincidental.net/comics/series/quasar/1-033.html |
|
Click to return to syllabus |
||
| Click to return to Growing Galaxies | hypertext |
Click to go to the Active Galactic Nuclei |